始于
分类:LeetCode
Tags: [ LeetCode ]
LeetCode 分类刷题 - 链表
按分类刷题,当前参考文章 https://labuladong.github.io/algo。
一些题目为二刷,以增强记忆、优化代码为主。
21. Merge Two Sorted Lists
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
// 要点 1
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);
auto p = dummy;
while (l1 != nullptr && l2 != nullptr) {
if (l1->val < l2->val) {
p->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
} else {
p->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
p = p->next;
}
// 要点 2
p->next = l1 != nullptr ? l1 : l2;
ListNode* ret = dummy->next;
delete dummy;
return ret;
}
}
要点:
- 创建一个伪头结点,避免后面代码特别处理两个链表的头。C++ 注意要把动态分配的内存释放掉。
- 尾部一定为二选一,不解释。
23. Merge k Sorted Lists
struct Cmp {
bool operator()(const ListNode* a, const ListNode* b) {
return a->val > b->val;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1);
auto p = dummy;
// 要点
priority_queue<ListNode*, vector<ListNode*>, Cmp> pq;
for (auto l : lists) {
if (l != nullptr)
pq.push(l);
}
while (!pq.empty()) {
auto front = pq.top();
pq.pop();
p->next = front;
if (front->next)
pq.push(front->next);
p = p->next;
}
ListNode* ret = dummy->next;
delete dummy;
return ret;
}
}
要点:
本题与 #21 唯一不同的地方在于需要使用优先队列。C++ 要构造一个存节点指针的优先队列比 Java 稍微麻烦一点,需要写一个 functor,上面的代码中为 Cmp。这个优先队列的顶,跟优先队列模板的 Compare 参数提供的 order 是相反的注意一下(我提供的是一个 greater 但是 top 返回给我的是小顶)。
141. Linked List Cycle
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
auto fast = head, slow = head;
// 要点 1
while (fast != nullptr && slow != nullptr) {
slow = slow->next;
// 要点 2
if (fast->next == nullptr)
return false;
fast = fast->next->next;
// 要点 3
if (fast == slow)
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
方法:
经典龟兔赛跑。
要点:
- 这题循环条件我看中文站官方题解好像可以用
slow != fast,这样的话循环外返回true应该是也可以。 - C++ 不能像 Java 一样莽着
.next。因为要访问 next 的 next 所以理所应当需要加一个判断。 - 本来我考虑了快慢指针撞结尾 null 的情况,但想了一下快指针永远在慢指针前面,所以撞是不可能撞的。
142. Linked List Cycle II
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
auto fast = head, slow = head;
while (slow != nullptr && fast != nullptr) {
slow = slow->next;
if (fast->next == nullptr) return nullptr;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow == fast) break;
}
// 要点 1
if (fast == nullptr) return nullptr;
// 要点 2
slow = head;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
};
要点:
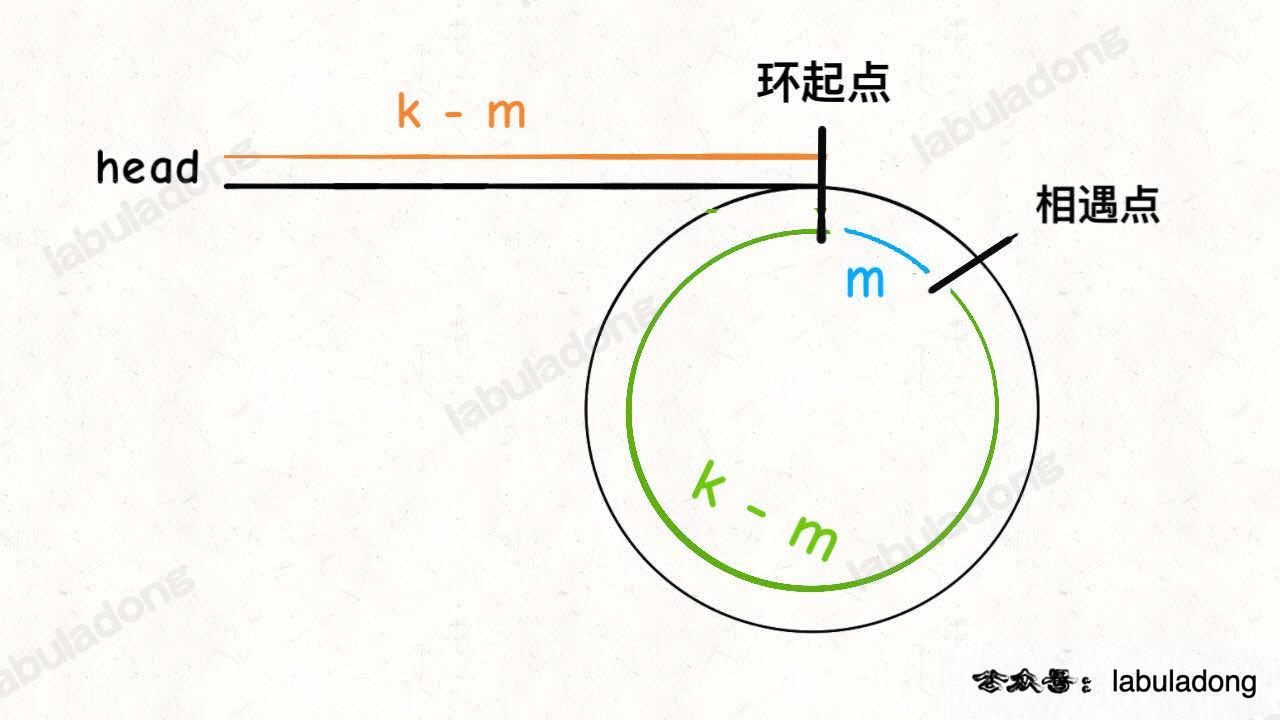
-
和 #141 不同的地方在于这里需要判断一下 fast 是否撞尾部了。不可能是 fast 的 next 撞,因为这样在第一个循环内已经 return 了。
-
这里用到的技巧是:
876. Middle of the Linked List
876. Middle of the Linked List
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* middleNode(ListNode* head) {
auto slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast) {
// 要点
if (!fast->next) break;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
};
要点:
同样是快慢指针,不同于上面那个代码,最后的结果依赖于 slow 的值,所以这里 if-break 的位置需要考究,这里必须在 slow 更新前 break,才能保证在奇数个节点时 slow 的位置正确。
19. Remove Nth Node From End of List
19. Remove Nth Node From End of List
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
// 要点 1
auto front = head, back = head;
while (n--) back = back->next;
// 要点 3
if (!back) {
auto next = head->next;
delete head;
return next;
}
// 要点 2
while (back->next) {
front = front->next;
back = back->next;
}
auto next = front->next;
front->next = next->next;
delete next;
return head;
}
}
要点:
- 前后指针。
- 确定我们要删除的不是
front->next而不是front。因为想删除front是不可能的。所以我这里选择判断 back 的下一项是否为 null,同理的方法还可以让 n 提前 -1 ,对应的代码修改逻辑也可。 - 为了保证要点 2 能够实现,要点 3 这里要特判 n 等于链表长度的情况。
160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists
160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
auto a = headA, b = headB;
// 要点
while (a != b) {
if (a) a = a->next;
else a = headB;
if (b) b = b->next;
else b = headA;
}
return a;
}
}
方法:
本题的方法就是把两个链表拼在一起,一前一后两种拼法分别遍历。
要点:
a 等于 b 其实包含两种情况,也就是结果的两种情况:其一是到达相交点时,其二是都为 null 时。
206. Reverse Linked List
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)
return head;
auto last = reverseList(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = nullptr;
return last;
}
}
方法:
last 里面存放的是原链表尾,也就是结果的链表头。这个代码比较神奇的地方就在于它一直在更新的是 head->next->next,这句话的意思就是把 head 的 next 的 next 更新为自己,也就是将自己与后一个节点的位置调换,递归地从后往前进行。
这里有一个我以前写的版本,需要用到一个额外的局部变量来存储链表最后一个节点,因为我的 reverse 递归返回的不能是头结点而是尾节点。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr) return head;
reverseListAux(head);
return ret;
}
ListNode* reverseListAux(ListNode* head) {
if (head->next == nullptr) return ret = head;
auto rev = reverseListAux(head->next);
head->next = nullptr;
rev->next = head;
return head;
}
private:
ListNode* ret;
};
92. Reverse Linked List II
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseN(ListNode* head, int n) {
if (n == 1) {
newHead = head->next;
return head;
}
auto last = reverseN(head->next, n - 1);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = newHead;
return last;
}
ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int left, int right) {
if (left == 1) {
return reverseN(head, right);
}
head->next = reverseBetween(head->next, left - 1, right - 1);
return head;
}
private:
ListNode* newHead;
};
吐槽:
II 是 92 题,I 是 206 题,II 在 I 前面。
方法:
首先实现 reverseN。与完全 reverse 不同的地方在于,原首部需要指向的不再是 null 而是第 n + 1 个节点,所以存储第 n + 1 个节点到 newHead 变量里面。
再就是递归实现 reverseBetween。基础情况为 left == 1,也就是直接做 reverseN(head, right)。left 大于 1 的情况,通过递归将 head 后移,可以完成 [left, right] 区间的逆转,然后一路上把 next 接起来,顺路的 next 还是保持原来的值,位于 left 的 next 接到新的头上。
25. Reverse Nodes in k-Group
class Solution {
public:
// 要点 1
ListNode* reverseRange(ListNode* head, ListNode* tail) {
ListNode *pre, *cur, *nxt;
pre = nullptr, cur = head;
ListNode* oldHead = head;
while (cur != tail) {
nxt = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nxt;
}
return pre;
}
ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {
if (!head) return nullptr;
auto p = head;
// 要点 2
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
if (!p) return head;
p = p->next;
}
// 要点 3
auto newHead = reverseRange(head, p);
head->next = reverseKGroup(p, k);
return newHead;
}
}
要点:
- 这里的函数
reverseRange,采用了迭代的方式对 [head, tail) 区间进行翻转,不接尾部,因为没用。 - 这个循环有两个作用,其一是判断剩余部分是否还有 k 个,另一是获得
reverseRange的参数tail的值。 - 递归衔尾。
注意一下这个算法的时间复杂度仅为 $O(N)$,空间复杂度为 $O(1)$。
234. Palindrome Linked List
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
auto fast = head, slow = head;
while (fast) {
slow = slow->next;
if (!fast->next) break;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
auto left = head, right = reverse(slow);
while (right) {
if (left->val != right->val)
return false;
left = left->next, right = right->next;
}
return true;
}
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* head) {
ListNode *pre, *cur, *nxt;
pre = nullptr, cur = head;
while (cur) {
nxt = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nxt;
}
return pre;
}
}
| 虽然很简单,但是 Easy 就有点说不过去了吧 (— — | )。比较好的解法是将中点之后的部分翻转即可,找中点用龟兔。如果不能破坏原链表结构可以用递归回溯: |
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
left = head;
return backtrace(head);
}
bool backtrace(ListNode* right) {
if (!right)
return true;
bool ret = backtrace(right->next);
ret &= (left->val == right->val);
left = left->next;
return ret;
}
private:
ListNode* left;
};
递归回溯的方法虽然直观,但是效率不是特别高。